How To Install Office Installer Mpkg Pkg
MPKG file is a Mac OS X Metapackage. A metapackage is an installation package that contains other installation packages. The enclosed packages can be component packages or metapackages (but not distribution packages). It may be either a single package or a metapackage. In the case of the metapackage, the packages which are part of the default install will be installed unless disqualified by a package's check tool(s). See man installer for the full functionality. Sudo installer -pkg /path/to/package.pkg -target / is all that's needed.
Office 2016 for Mac comes in an installer package that has been causing several issues for Mac sysadmins deploying it in their organizations. At least a coupleposts exist already for how to “fix” the installer and deploy the software, but I haven't seen anyone actually detail some of these issues publicly. The best way to “fix” the installer is to have Microsoft fix it so that it can be deployed the same way we deploy any other software. Office is probably the most common software suite deployed in organizations, and so it's a very bad sign that 2016 for Mac has begun its life as an installer that cannot be deployed without workarounds and/or repackaging.
In this post, as usual I'll go into some detail about this installer's problems, review some known workarounds and propose some solutions.
Client software deployment tools
Microsoft provides Office 2016 for Mac in two flavors: one for Office365 subscribers which users can “activate” by signing into their O365 accounts, and one for organizations entitled to a volume license through some agreement. The volume license is activated during the install process, very similar to Office 2011. Volume licensed copies of software are often installed within organizations using automated deployment tools like Munki or Casper. These tools make it possible for IT to deploy the software without numerous manual steps on each client, and control when the software is made available and in what context (i.e. do users install on their own via a self-service system, is it installed automatically at the time the machine is deployed to a user, or later on a schedule, etc.).
There are several ways in which the context of such deployment tools install software is different than that of a user manually installing software onto his or her own personal machine (where the user also has admin privileges), but two important ones are:
- If installing a standard OS X installer package (.pkg, .mpkg), the installation will take place by some invocation of the
installercommand-line tool. This happens to set an environment variable,COMMAND_LINE_INSTALL, which is not present if an installer package is double-clicked and run using the standard Installer UI. Installer scripts may make use of this to adjust their behavior accordingly. - The installation may take place while no user is logged in, and the machine is waiting at the login window. This may be so because a machine has just had its OS installed or re-imaged, and the deployment tools are now automatically installing all the other software destined for this machine. A software may also require a logout or restart, and therefore the deployment tools may opt to first log the user out so that the software can be installed.
Office 2016's licensing packages
The volume license installer is provided as a Distribution installer package, which includes two components that specifically pertain to licensing: 1) com.microsoft.pkg.licensing, and 2) com.microsoft.pkg.licensing.volume. You can inspect these packages yourself using a GUI tool like Pacifist or the Suspicious Package QuickLook plugin, or even simpler by using the pkgutil tool that's built-in to OS X, and just expand the flat package to a temporary directory:
pkgutil --expand '/Volumes/Office 2016 VL/Microsoft_Office_2016_Volume_Installer.pkg' /tmp/office2016
The com.microsoft.pkg.licensing package installs a LaunchDaemon and PrivilegedHelperTool, which provides infrastructure necessary to allow an application to perform the license activation without needing to ask for administrative privileges. This allows the licensing to be performed by any user on the system, and to store an “activation status” in a location that would normally required admin or root privileges. The package also runs a postinstall script that loads the LaunchDaemon, and if the installer was run within the GUI, the bundled dockutil is invoked to add items to the user's dock.
The com.microsoft.pkg.licensing.volume package installs an application, “Microsoft Office Setup Assistant.app,” to /private/tmp, and runs a postinstall script that runs the binary within this application bundle using sudo, so as to run the command as the user who is logged in. Finally, it removes this application bundle it just installed and exits 0, so that the installation will not be aborted if this process fails (even though the rm command, given the -f flag, should not exit anything other than 0). To know what user is logged in - or the user the script assumes is logged in - it reads the USER environment variable.
Installing Office at the login window
In a command-line install, $USER will be the user running the installer command, and this will likely be root. But this is a side detail. Remember the earlier point about installations not necessarily being performed while a user is logged in? Here is what we see in /var/log/install.log if we invoke the installer while no user is logged in, via SSH, using a command like installer -pkg /path/to/Office2016.pkg -tgt /:
The last line, FAILED TO establish the default connection to the WindowServer, _CGSDefaultConnection() is NULL, tells us that the application being run by the com.microsoft.pkg.licensing.volume package, Microsoft Office Setup Assistant, is an application that assumes it will be able to access a GUI login session, despite it not actually having any window elements that are normally shown to the user. If you run the Office 2016 installer normally in a GUI installer, you may notice this item bounce up in the dock ever so briefly in order to validate and write out a license file to disk. But in an automated installation at the loginwindow, this process starts and then stalls forever, with a process you can find yourself from running ps auxwww, a line which looks like:
/usr/bin/sudo -u root /private/tmp/Microsoft Office Setup Assistant.app/Contents/MacOS/Microsoft Office Setup Assistant
If I retry the above using Apple Remote Desktop as the package installation tool rather than SSH and installer, the process stalls but I see no error about the failure to connect to the WindowServer, presumably because the installation through ARD causes USER to be considered nobody:
/usr/bin/sudo -u nobody /private/tmp/Microsoft Office Setup Assistant.app/Contents/MacOS/Microsoft Office Setup Assistant
So if the Microsoft Office Setup Assistant tool is hanging during the installation, one might be prompted to use choiceChangesXML with installer so that the problematic package component can be skipped, and the installation can complete successfully.
Office 2011
Office 2011 had a similar issue with its license subsystem, where if Office was installed and updated at the loginwindow (say, on any fresh machine install) without a manual launch in between to at least “initialize” the activation, applications would behave as if Office was not activated at all. The solution, which manyorganizations employed, was to capture the license storage plist from /Library/Preferences on a known good machine, and redeploy this same license file along with an installation of Office 2011, either a new install or one with the broken licensing issue. Many people have already found that this same approach - capturing the license file in /Library/Preferences/com.microsoft.office.licensingV2.plist and deploying this as a separate package is enough for Office 2016 to consider itself volume-licensed.
I've had to implement this solution for Office 2011 before, but it seems ridiculous that an application so widespread, with so much engineering behind it, can't be installed at the loginwindow without having its licensing data severed - especially given that the licensing procedure doesn't actually require any user input. The licensing tool runs, and the machine is now licensed. However, with a functioning, standard install, the licensing data is unique per machine. I dislike the idea of messing with (and repackaging, and redeploying) data that normally I should not need to know or care about, for which the application should be responsible, and which if something goes wrong the consequences are serious: Office ceases to function, or instead prompts users to sign in with O365 credentials to activate Office.
More issues
Oh, but this is not even the only issue with the Office 2016 installer. There is also an auto-update daemon that Microsoft adds to the LaunchServices database using an undocumented -register flag to the lsregister binary. This command is also run using sudo -u $USER, but only if not doing a command line install. It looks like the install script is trying to do the right thing by not doing some user-specific tasks (this lsregister command performs a change to the LaunchServices database for the user running the command) during a CLI install, however if this auto-update daemon is not manually registered in LaunchServices, the user will see a confusing dialog the first time they open any Office application and it checks for updates (as it does by default):
This is another roadblock that a sysadmin will definitely want to avoid, and yet what is the solution? The postinstall script for the com.microsoft.package.Microsoft_AutoUpdate.app component package contains this in the postinstall script:
One possible workaround is oddly appealing: don't install the volume license combined install package at all! Office 2016 updates are actually full application installers, one for each application update. These don't contain any of the licensing or auto-update related infrastructure that is included in the VL installer. Office 2016 applications will either use the Microsoft Auto-Update (MAU) tool that might be on the system already with Office 2011 if it exists, or if MAU doesn't seem to exist on the system, the applications will simply not offer any interface with which to check for updates. Most sysadmins that deploy software might like this option anyway, while others might prefer that there is still a means to perform updates ad-hoc, or expect users to all the applications to update on their own.
Some experimenting with the lsregister command hints at other options for trusting other “domains,” references to which I can find only on Charles Edge's blog:
sudo /System/Library/Frameworks/CoreServices.framework/Frameworks/LaunchServices.framework/Support/lsregister -domain system -domain user -domain local -trusted /Library/Application Support/Microsoft/MAU2.0/Microsoft AutoUpdate.app/Contents/MacOS/Microsoft AU Daemon.app
Perhaps it is possible to “globally” register this daemon in these various domains so that a user doesn't need to individually register the daemon. Or perhaps a login script might be required to invoke this command at login time for every user, using a tool like outset. Or perhaps admins will simply opt to not install MAU at all, so as to avoid this whole mess.
Patrick Fergus even posted this exact issue to Microsoft's community forums four months ago, with no response.
Complain More
I've quickly skimmed over two issues with the Office 2016 for Mac volume license installer, and have alluded to various workarounds that all involve some kind advanced trickery: using obtuse Installer choiceChangesXML overrides to avoid problematic packages, copying licensing plists from one machine to another, and modifying scripts that invoke under-documented OS X command-line tools with undocumented options. Others online who have posted about these issues have incorporated these into repackaging and custom scripts.
If you wrote the installer packages and scripts for a product like Microsoft Office, how would you feel if you found out that your product was non-deployable in its factory state, and that potentially thousands of sysadmins were breaking apart your packages and putting them back together in ways you never expected, making guesses about how your updates will be structured in the future, and bypassing your licensing creation mechanism altogether? Would you want to support an installation like this?
It's important to understand the mechanisms being used when installer scripts are involved in software you deploy and support in your organization. It's unfortunate that some of the most widely-used software also happens to be challenging to deploy, and the amount of effort required to convince vendors that there are issues - even just to get in contact with an actual release engineer - can be maddening at times. But if admins continue to quietly work around major issues like this, we cannot expect the situation to change.
So, escalate the issue through whatever supported channels are available to you. If you are a Microsoft Enterprise customer and have a Technical Account Manager, this seems to be the recommended route. If you're paying for support, make it worth it. Tweet at and e-mail people who might care and may be in a position to effect change.
Provide hard data about why it impedes your ability to install the software in a supported manner, and the scope of the impact, including the number of machines. Demonstrate that you cannot use supported tools like Apple Remote Desktop, or a paid management tool like Casper, to deploy their software without needing to perform destructive changes to their packages, or deploy “updates” as the base installation and copy a “golden master” licensing plist to all machines just to have the software function. Give specific examples about where the issues lie: suggest that their Setup Assistant tool be fixed so that it may be run purely at the command-line with no GUI login session required; suggest they devise a more robust way of handling the AU Daemon trust issue, so that a command-line install can result in an installation that's functionally the same as a manual GUI-driven installation.
- The Office for Mac 2016 Volume License Installer, Two Months Later –
- Disabling First-run Dialogs in Office 2016 for Mac –
- Adobe Creative Cloud Deployment - Packaging a License File –
- How to Package Profiles –
- 1.Symbian Package File
- 2.PlayStation Store Downloaded Package
- 3.Mac OS X Installer Package
- 4.CoCreate OneSpace Modeling Package File
- 5.Midtown Madness 2 Model File
File Type 1Symbian Package File
| Developer | Nokia |
| Popularity | |
| Category | Settings Files |
| Format | Text |
What is a PKG file?
A PKG file is a text file required to build an .SIS installer file, which is used to install applications on devices running the Symbian operating system (OS). It contains installation information in plain text that defines how to build the SIS installer file. PKG files typically include information about the languages supported by the application, vendor name, software dependencies, application files to copy, and details for digitally signing the file to verify its contents.
You will most likely only encounter Symbian PKG files if you are developing an application for the Symbian OS. The PKG file must be defined by Symbian developers in order to build a single distributable SIS installer file. When the application is ready to be built, developers typically use the 'makesis' command, which is part of the CreateSIS utility. Developers may also use the Sisar or Easy SIS Creator applications, which provide a GUI for building SIS files.
Since PKG files are saved in plain text, they can be opened and modified with a text editor, such as Microsoft Notepad or Apple TextEdit, which are bundled with Windows and macOS. If you cannot open the PKG file with a text editor, you most likely have a different type of PKG file. This is due to various file types using the .pkg file extension, which includes the macOS Installer Package and PlayStation Store Download Package formats.
While SIS files are used to install applications, you can unpack the files if you want to view their contents. You can use the free UnSIS tool to unpack SIS files.
NOTE: In 2010, the Symbian Foundation ended and the Symbian OS was discontinued. Nokia eventually stopped accepting software from developers in 2014.
Unknown files on your Mac? Try File Viewer.| Mac |
|
| Windows |
|
| Linux |
|
File Type 2PlayStation Store Downloaded Package
| Developer | Sony |
| Popularity | |
| Category | Game Files |
| Format | N/A |
.PKG File Association 2
A PKG file is a file downloaded from Sony's PlayStation Store, an online store with games, movies, and demos for PS3 and PSP devices. It is saved in an encrypted format that is only recognized by compatible Sony devices and is used specifically for downloadable games, game updates, and demos.
Packages downloaded from the PlayStation Store can be transferred to a PSP or PS3 via USB, Memory Stick, or a network connection.
| Mac |
|
| Windows |
|
File Type 3Mac OS X Installer Package
| Developer | Apple |
| Popularity | |
| Category | Compressed Files |
| Format | Binary |
.PKG File Association 3
A PKG file is a package of compressed installer files used to install a software program. It is commonly used for installing software in Mac OS X and may be installed individually or referenced by an installer script included with the software.
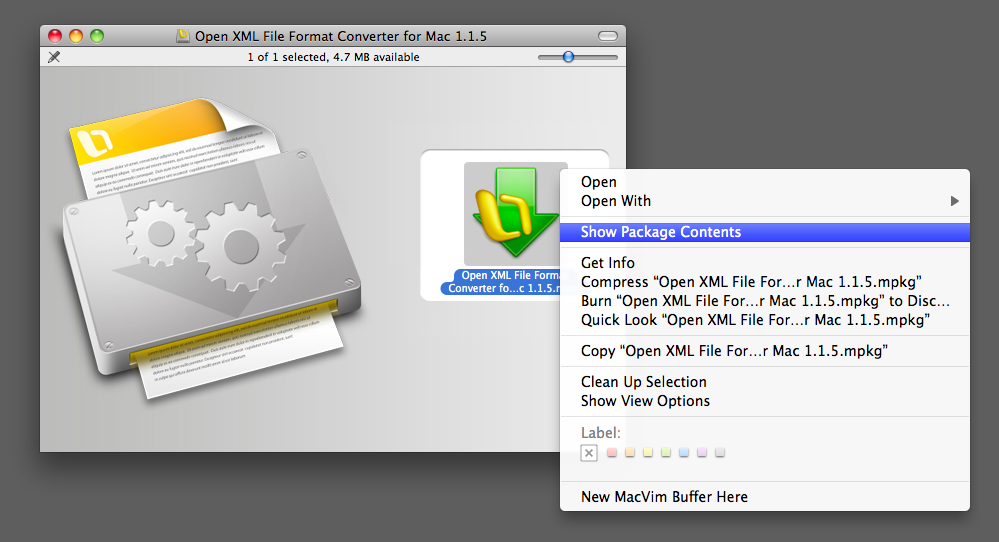
Double-click the package to install the files. Right-click (Control-click) and select 'Show Package Contents' to view the files stored in the package. Apple Installer is the built-in utility for opening PKG files included with Mac OS X.
| Mac |
|
File Type 4CoCreate OneSpace Modeling Package File
| Developer | Parametric Technology |
| Popularity | |
| Category | 3D Image Files |
| Format | Zip |
.PKG File Association 4
File created by CoCreate software programs, which are used for 3D modeling; contains the files for a 3D model in a compressed format; used to reduce the size of a model design for transferring over the Internet.
PKG files in Modeling 2005 or earlier use proprietary and CPIO (.CPIO files) compression. PKG files in Modeling 2006 and later use Zip compression.
NOTE: CoCreate OneSpace Modeling is now known as CoCreate Modeling. It was also previously known as OneSpace Designer Modeling and SolidDesigner.
| Mac |
|
| Windows |
|
File Type 5Midtown Madness 2 Model File
| Developer | Microsoft |
| Popularity | |
| Category | 3D Image Files |
| Format | Binary |
.PKG File Association 5
Game data file used by Midtown Madness 2 (MM2), a 3D racing game; saves a 3D model of a car; located within .AR game archives and can be edited with ZModeler.
Knight Rider 2 free download video game for Windows PC. Download free full version “Knight Rider 2” from Gameslay. The game setup is tested and 100% fully working PC Game for free Download. The direct/torrent download from Gameslay.net is highly compressed and free of any virus, spyware or adware. Knight Rider 2 (Video Game) Review Knight Rider 2 is racing video game. Knight rider 2 torrent download.
| Windows |
|